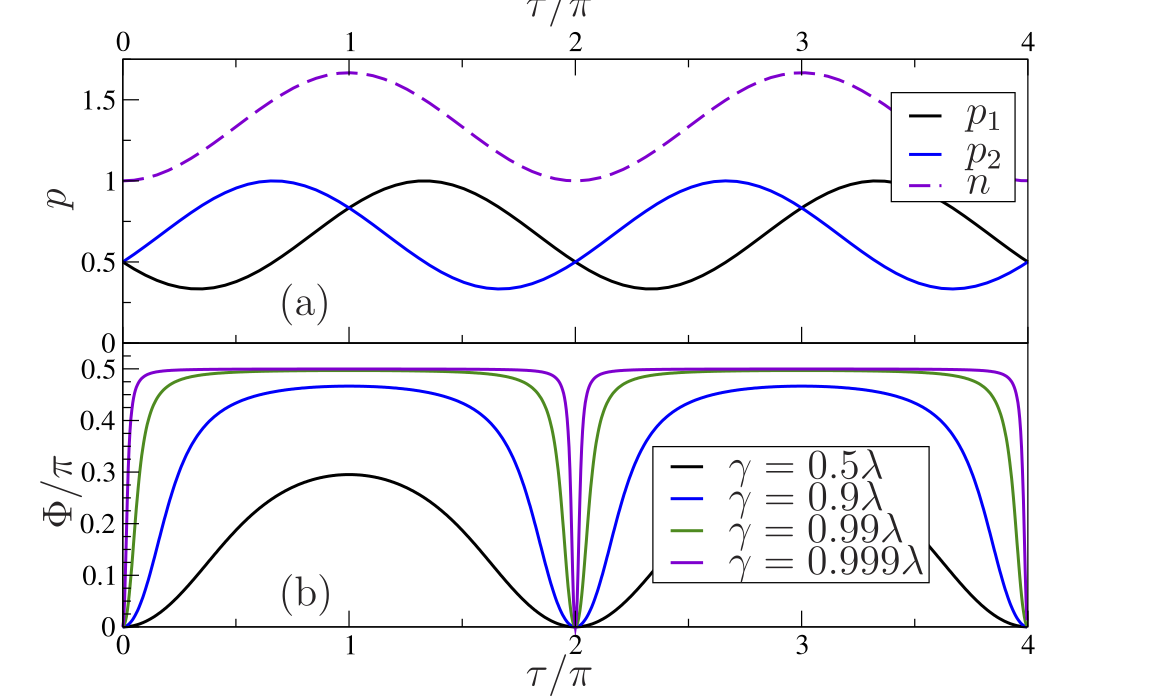
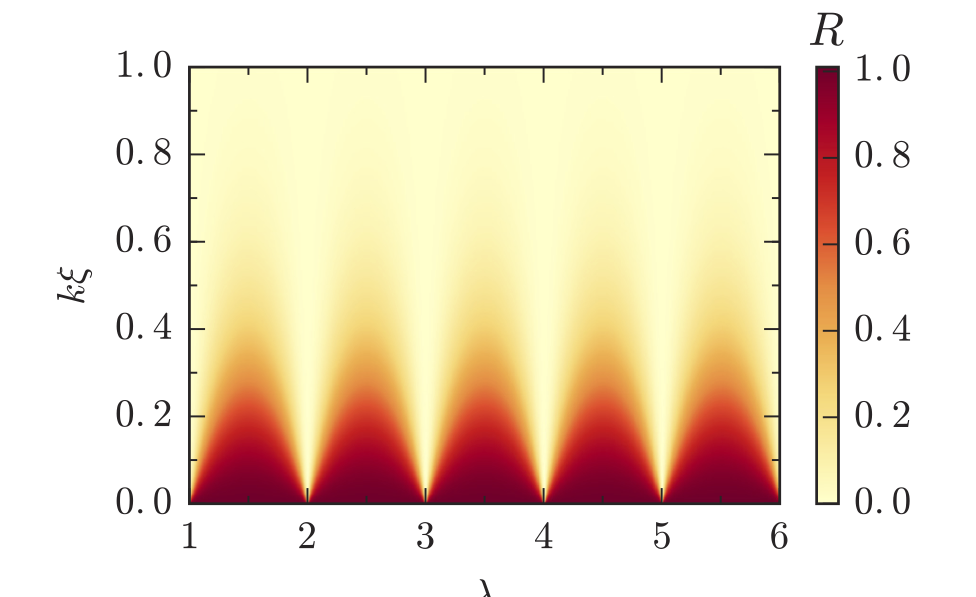
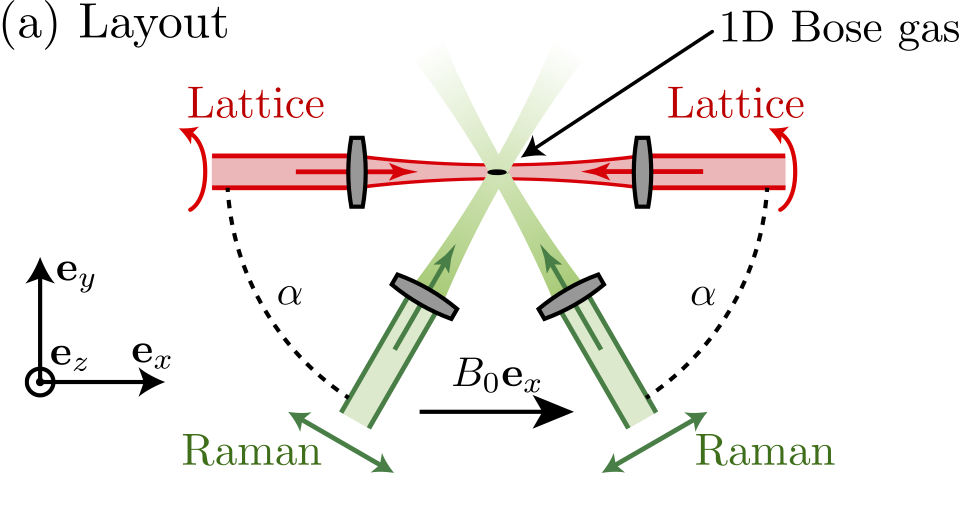
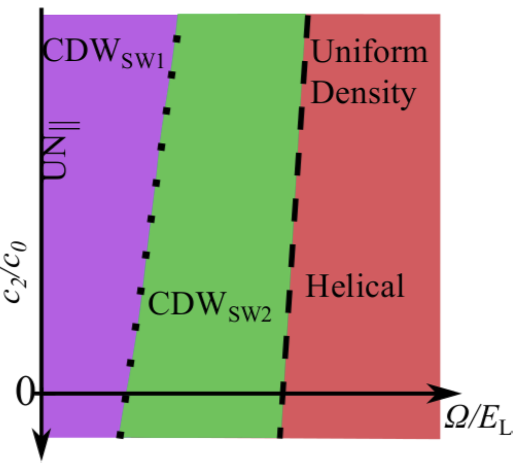
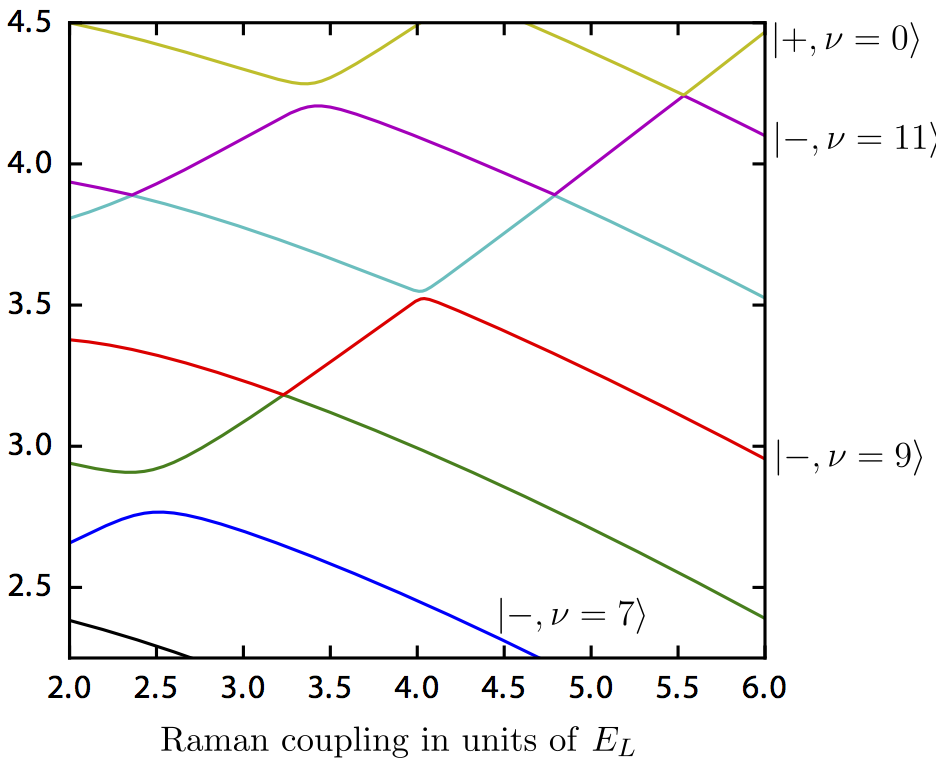
Perpetual emulation threshold of PT-symmetric Hamiltonians
We describe a technique to emulate the dynamics of two-level PT-symmetric spin Hamiltonians, replete with gain and loss, using the unitary dynamics of a larger quantum system. The two-level system in question is embedded in a subspace of a four-level …
Perpetual emulation threshold of PT-symmetric Hamiltonians Read more »