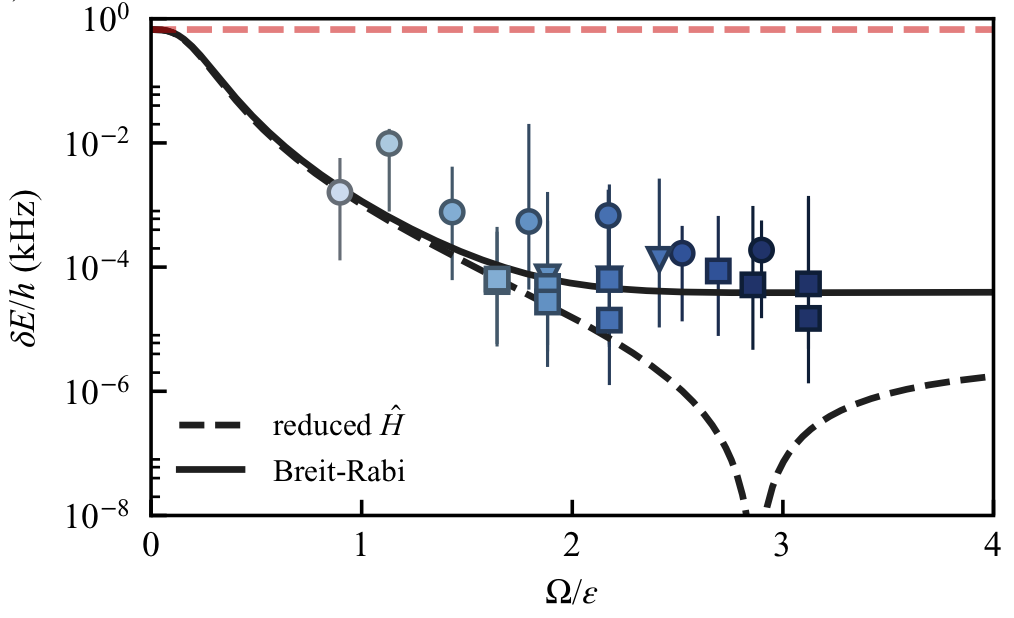
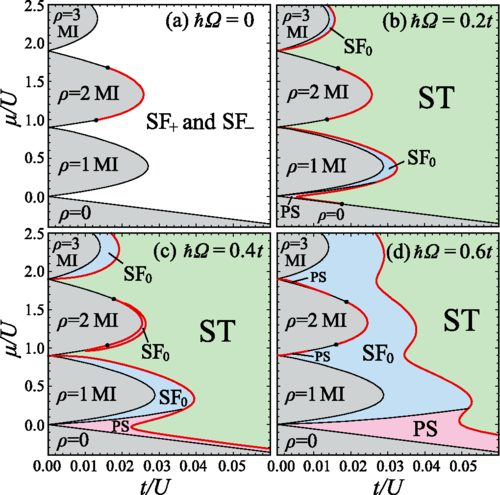
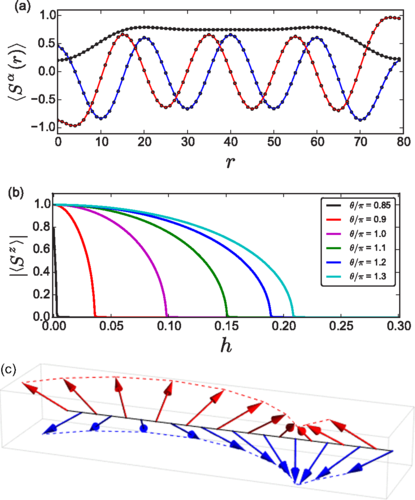
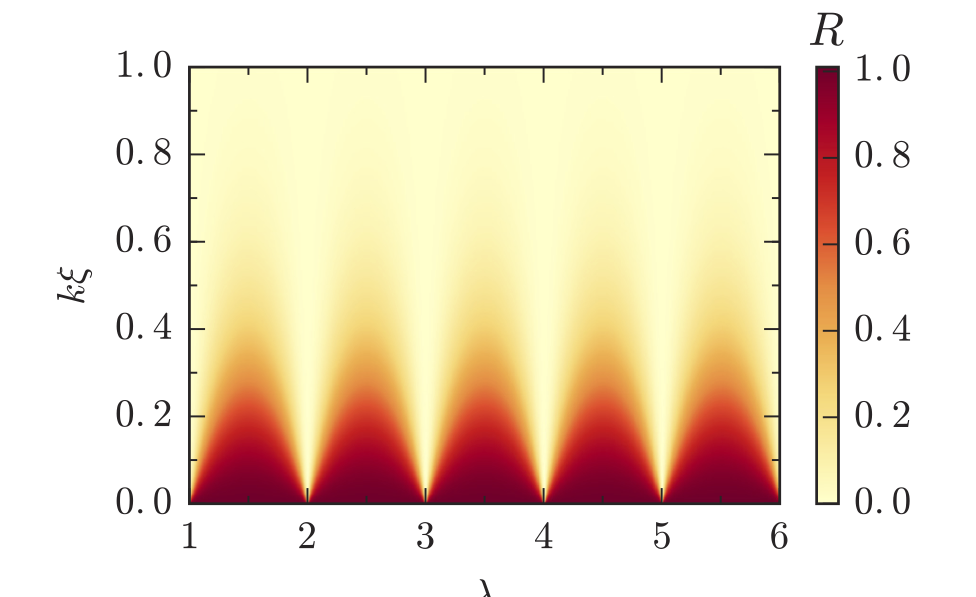
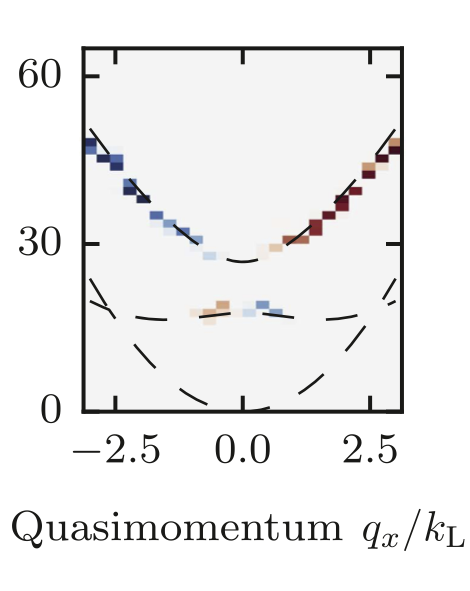
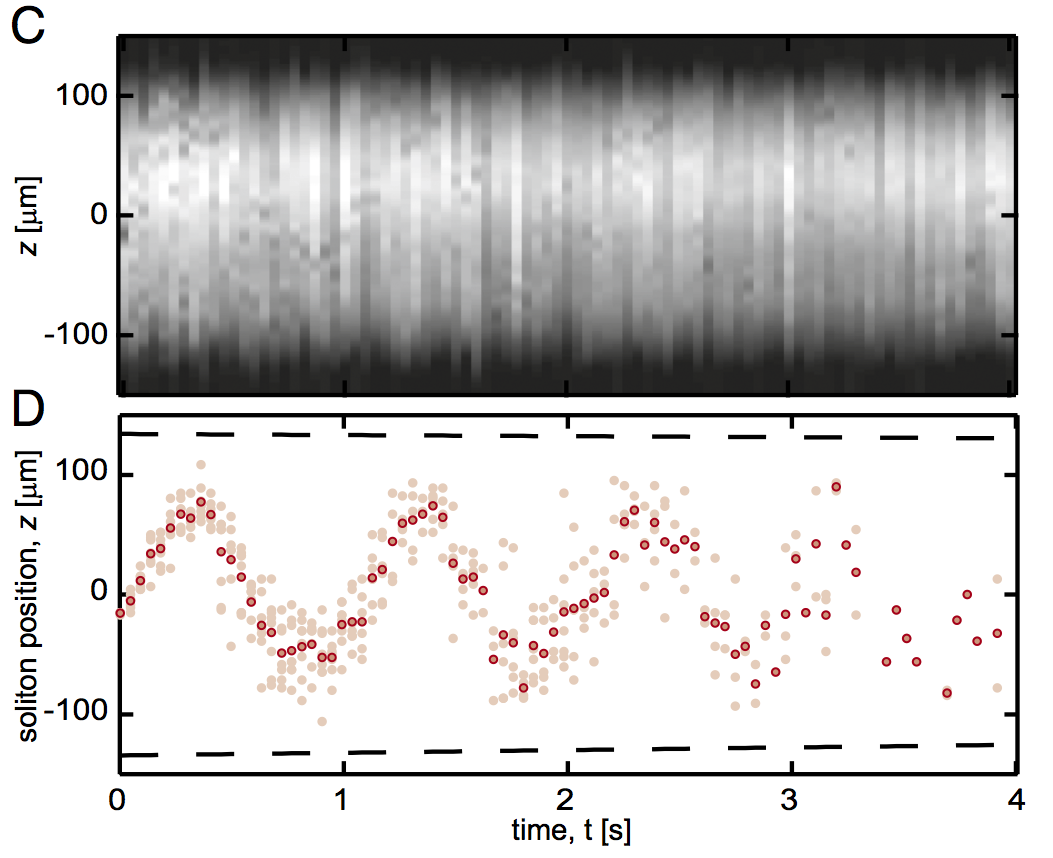
Synthetic clock transitions via continuous dynamical decoupling
Decoherence of quantum systems due to uncontrolled fluctuations of the environment presents fundamental obstacles in quantum science. Clock transitions which are insensitive to such fluctuations are used to improve coherence, however, they are not present in all systems or for …
Synthetic clock transitions via continuous dynamical decoupling Read more »