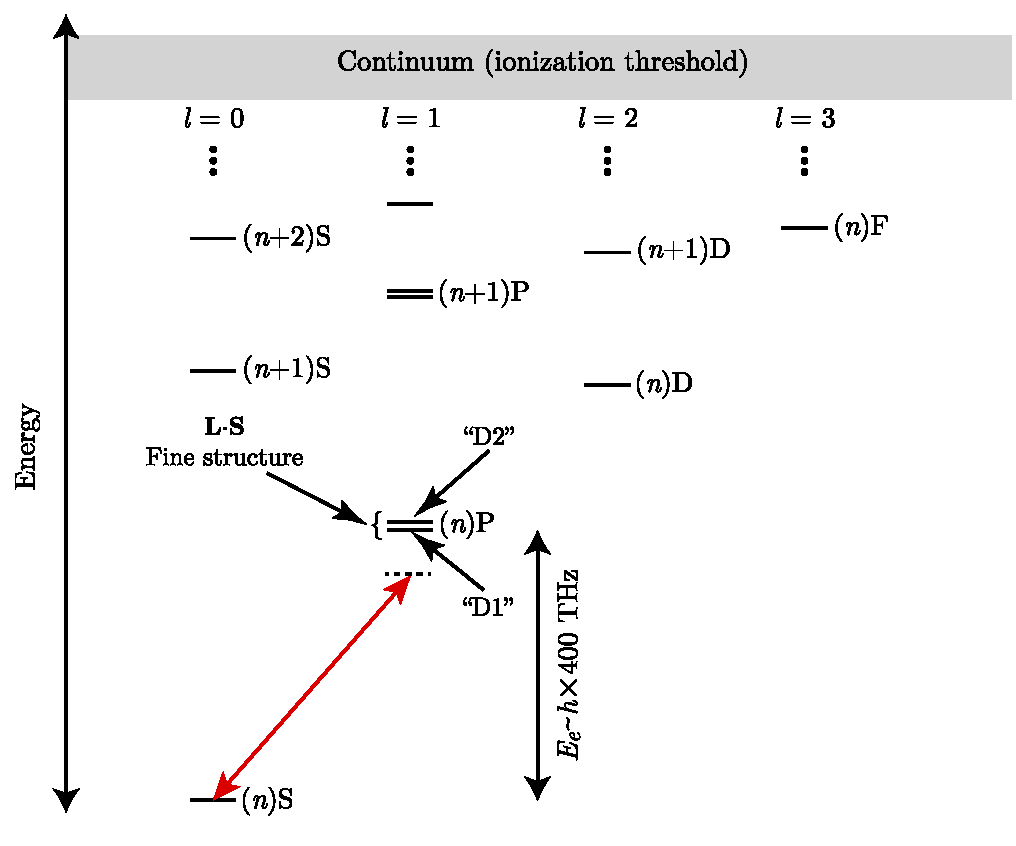
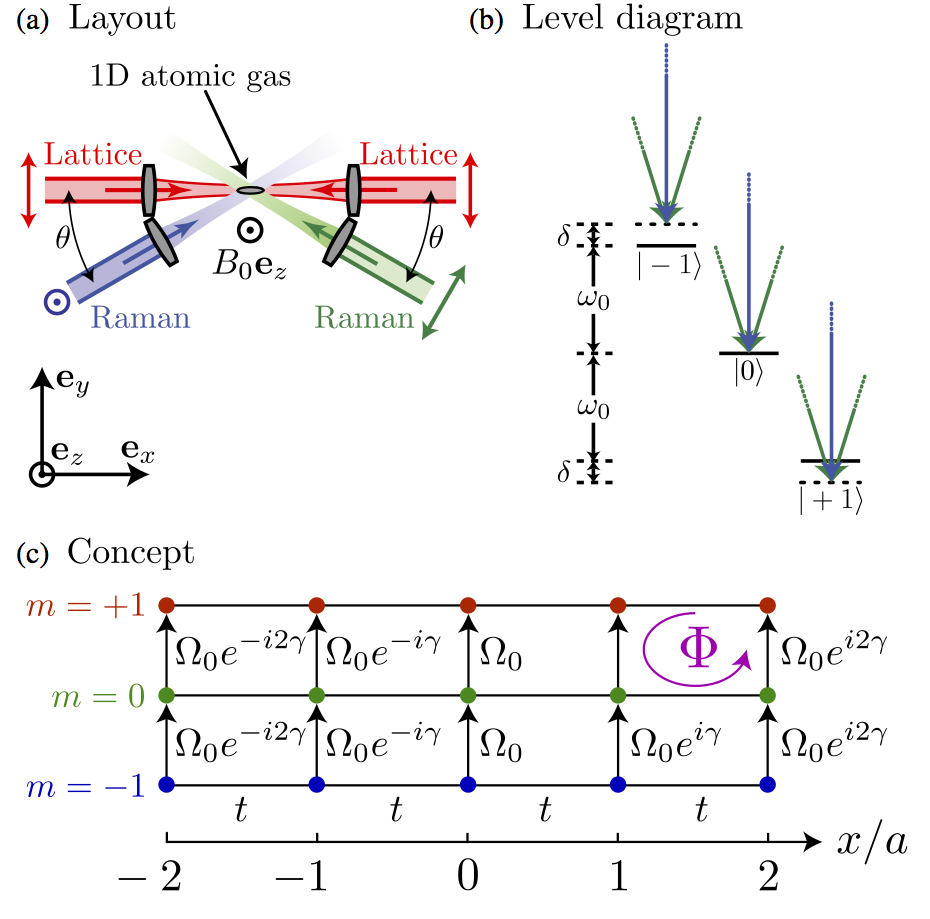
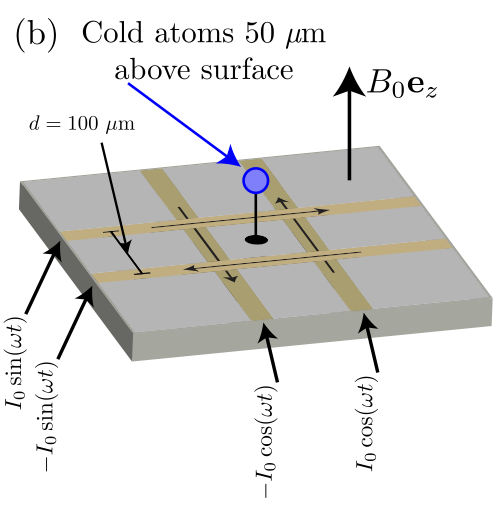
Tutorial: Synthetic gauge potentials for ultracold neutral atoms
Synthetic gauge fields for ultracold neutral atoms—engineered using the interaction between laser fields and the atoms’ internal ‘spin’ degrees of freedom—provide promising techniques for generating the large (synthetic) magnetic fields required to reach the fractional quantum Hall (FQH) limit in …
Tutorial: Synthetic gauge potentials for ultracold neutral atoms Read more »