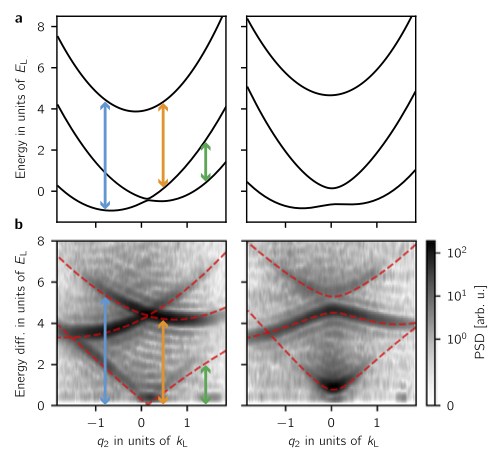
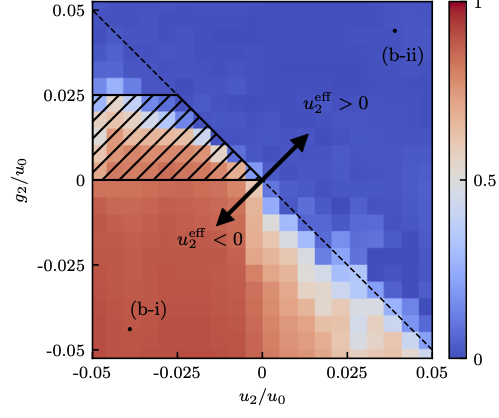
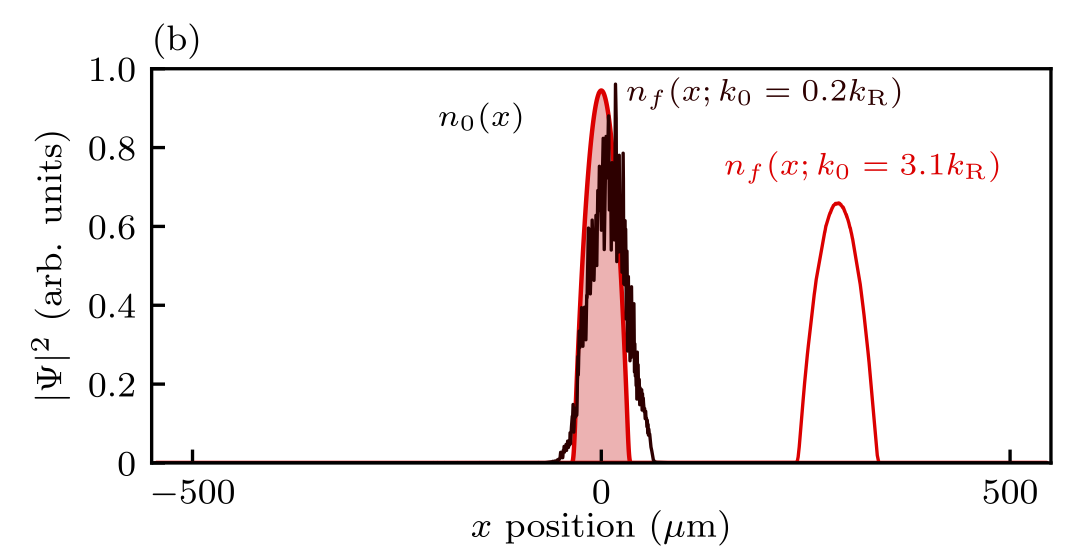
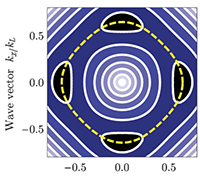
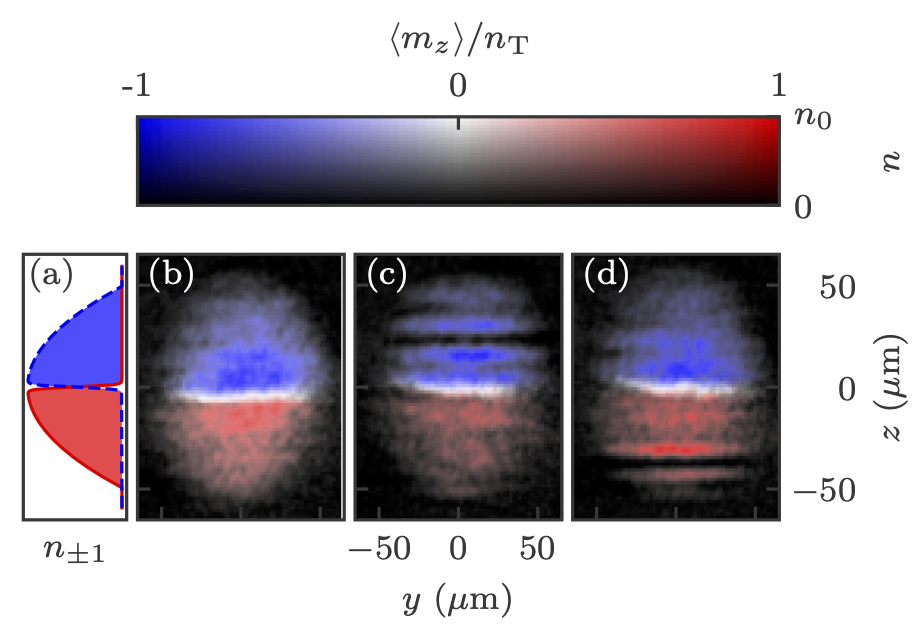
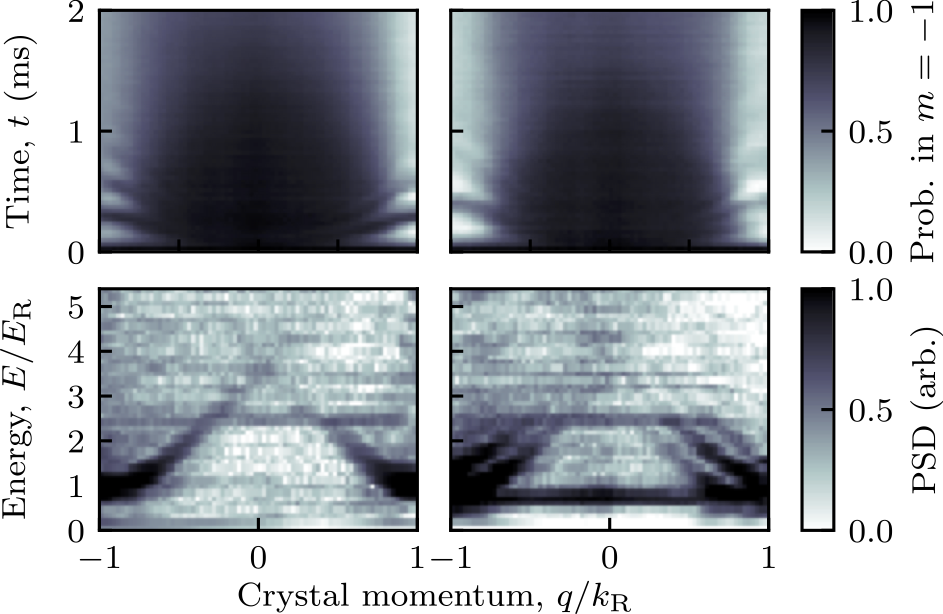
JQI writeup of: Topological features without a lattice in Rashba spin-orbit coupled atoms
Spielman group alumna Dr. Dina Genkina has composed a high level write-up of Dr. Ana Valdés-Curiel’s Rashba paper! https://jqi.umd.edu/news/researchers-comb-atoms-into-novel-swirl Topological features without a lattice in Rashba spin-orbit coupled atoms; A. Valdés-Curiel, D. Trypogeorgos, Q.-Y. Liang, R. P. Anderson, and I. …