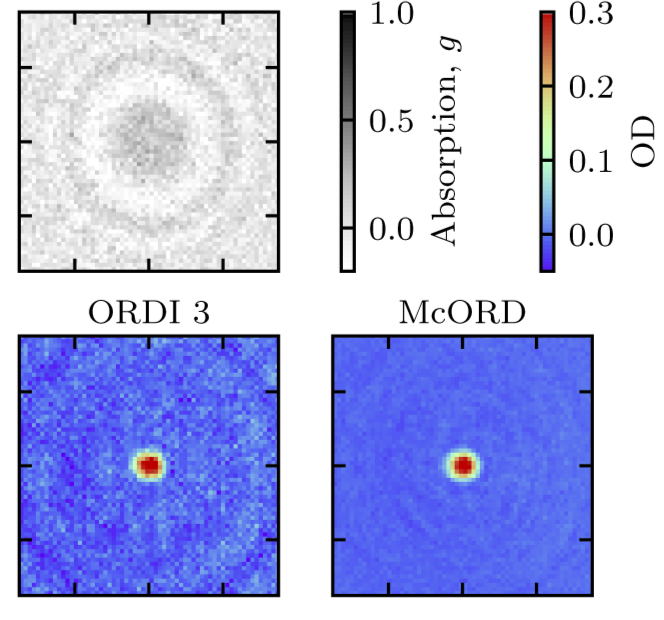
Self-Bayesian aberration removal via constraints for ultracold atom microscopy
High-resolution imaging of ultracold atoms typically requires custom high numerical aperture (NA) optics, as is the case for quantum gas microscopy. These high NA objectives involve many optical elements, each of which contributes to loss and light scattering, making them …
Self-Bayesian aberration removal via constraints for ultracold atom microscopy Read more »